In recent years, NAD⁺ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, commonly known as Coenzyme I) has maintained steady popularity in the anti-aging field. From groundbreaking anti-aging studies in top global academic journals like Cell, Nature, and Science, to major corporations such as Bezos and Google flocking to invest in the longevity industry focused on anti-aging research, even domestic news like Pan Shiyi sharing his NAD⁺ supplement consumption experience and Li Ka-shing investing in NAD⁺-related industries have made NAD⁺ a focal point of public attention, thanks to its core potential to regulate the aging process and support anti-aging efforts.
As NAD⁺’s popularity grew, various NAD⁺-related anti-aging supplements also gained traction. Among them, NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) quickly became the mainstream anti-aging supplement by branding itself as a "direct precursor of NAD⁺". But many people wonder: if the ultimate goal is to supplement NAD⁺ for anti-aging, why not take NAD⁺ directly instead of NMN? What exactly is the difference between NMN and NAD⁺ when it comes to anti-aging effects? Today, we’ll break down the distinctions between NMN and NAD⁺ from core perspectives like scientific principles, NAD⁺ absorption effectiveness, and practical anti-aging usability to help you find the right anti-aging approach for yourself.

First, it’s important to clarify a key premise for anti-aging supplementation: NAD⁺ naturally exists in every cell of our body as a core coenzyme. It’s indispensable for thousands of physiological processes closely related to anti-aging, including metabolism, DNA repair, and gene regulation. However, as we age, NAD⁺ levels in the body drop steadily—one of the core reasons we experience aging signs and a key target for anti-aging interventions. Theoretically, direct NAD⁺ supplementation seems like the most straightforward anti-aging method, but in practice, it simply doesn’t work for anti-aging purposes—the problem lies in "absorbability" of NAD⁺.
NAD⁺ has a relatively large molecular weight (663.43g/mol) and an unstable molecular structure, making it unable to directly cross cell membranes to be absorbed and utilized by cells for anti-aging effects. When we take oral NAD⁺ supplements for anti-aging, most of the NAD⁺ is broken down into small molecules like nicotinamide (NAM) in the digestive tract. Only a tiny fraction of the original NAD⁺ can enter cells and be converted into active NAD⁺, resulting in extremely poor NAD⁺ supplementation effectiveness that fails to achieve the desired anti-aging effect.
NMN, as a "direct precursor of NAD⁺", perfectly solves this NAD⁺ absorption problem for anti-aging supplementation. With a smaller molecular weight (334.22g/mol) and more stable structure, NMN can efficiently enter cells through specific transport channels on the cell surface. After a simple catalytic reaction, NMN is converted into NAD⁺, with much higher NAD⁺ supplementation efficiency than direct NAD⁺ intake. That’s why NMN is now the preferred choice for most people looking to supplement NAD⁺ for anti-aging.
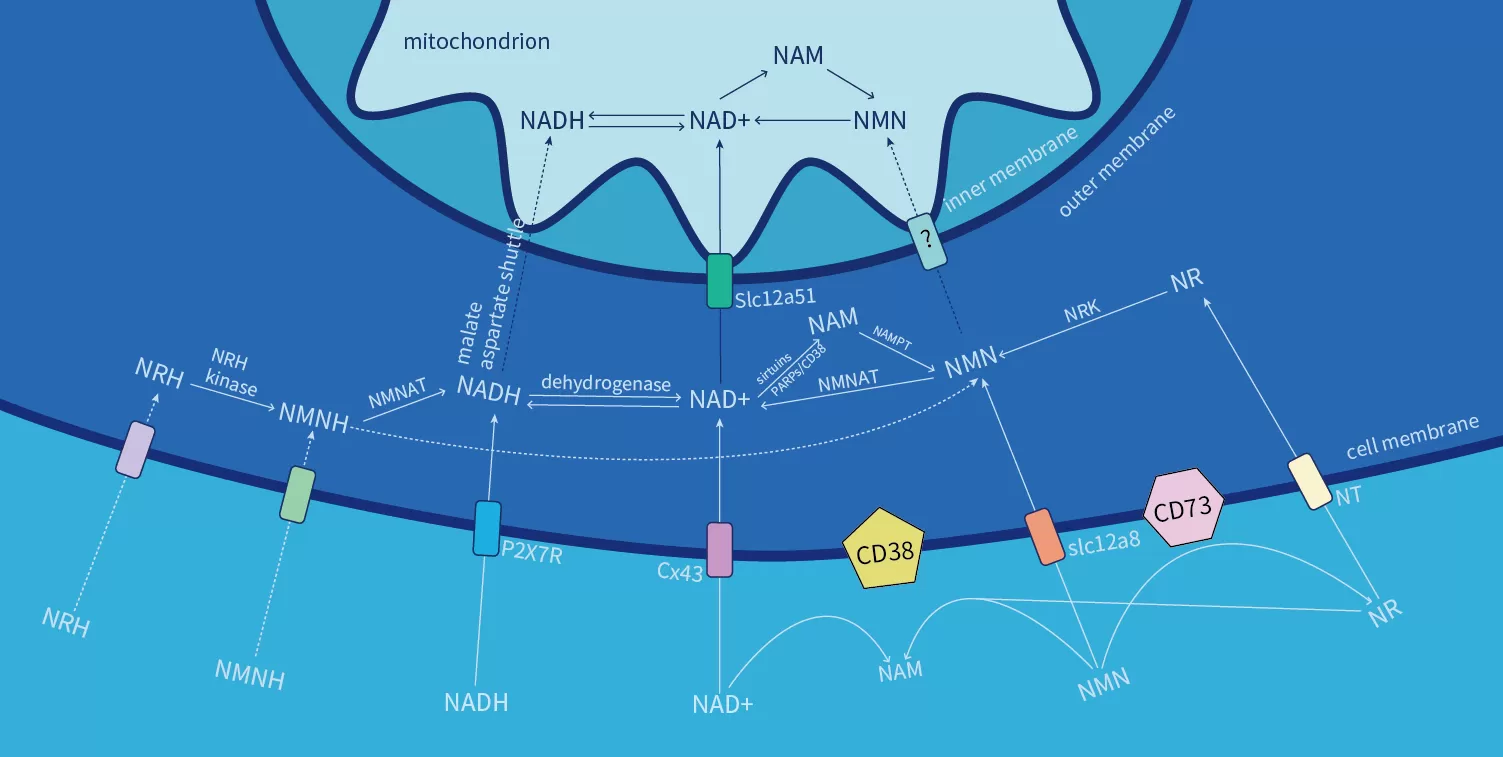
Beyond the core difference of "whether direct NAD⁺ supplementation is possible for anti-aging", NMN and NAD⁺ also vary significantly in NAD⁺ absorption methods, anti-aging action processes, and practical anti-aging effectiveness. Let’s break them down one by one to clarify which is better for your anti-aging goals:
NMN has a clear and efficient absorption pathway for NAD⁺ supplementation: it can directly enter cells through the dedicated Slc12a8 transporter on the cell membrane, without going through complex decomposition and resynthesis processes that waste anti-aging ingredients. Although a small portion of NMN is broken down by glycosidases (such as CD38 and CD73) on the cell membrane surface—enzymes that also consume NAD⁺—most of the NMN enters cells in its intact form to convert into NAD⁺ and exert anti-aging effects.
NAD⁺, however, is different for anti-aging use. Due to its large molecular weight and unstable structure, NAD⁺ cannot directly enter cells through membrane transporters to deliver anti-aging benefits. After oral intake of NAD⁺ supplements, the NAD⁺ is first broken down into basic components like nicotinamide and adenine by digestive enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract. Once these components enter cells, they require multiple enzymatic reactions (relying on rate-limiting enzymes like NAMPT) to resynthesize NMN, which is then converted into NAD⁺. This process is not only cumbersome but also results in significant NAD⁺ losses. The final proportion of active NAD⁺ produced is extremely low, making direct NAD⁺ supplementation costly and ineffective for anti-aging.
In terms of action logic, both ultimately aim to increase intracellular NAD⁺ levels, but their processes are completely different:
NMN works through "indirect NAD⁺ supplementation" for anti-aging: After entering cells, NMN is converted into NAD⁺ in one step under the catalysis of NMNAT (nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase), directly increasing intracellular NAD⁺ concentration—the key to activating anti-aging pathways. This increased NAD⁺ in turn provides energy for core anti-aging pathways involving sirtuins (longevity proteins) and PARP (DNA repair enzymes), which are critical for slowing aging. Simply put, NMN is like a "semi-finished product" of NAD⁺ for anti-aging—once inside cells, it only needs a little processing to become active NAD⁺ that drives anti-aging effects.
NAD⁺, on the other hand, acts "directly" for anti-aging if it can reach cells: If NAD⁺ can successfully enter cells, it can act as a coenzyme in various anti-aging-related physiological reactions without further conversion. But as we mentioned earlier, NAD⁺ struggles to cross the cell membrane barrier—most of the NAD⁺ from supplements never reaches the cells, so it can’t exert its direct anti-aging effects. It’s like having the best anti-aging fuel in the world but being unable to deliver it to the engine (cells); in the end, it’s just a waste of money with no meaningful NAD⁺ supplementation or anti-aging effect.
From clinical research and real-world user experiences, NMN’s effectiveness for NAD⁺ supplementation and anti-aging has been well-verified: Multiple clinical studies have shown that oral NMN can increase NAD⁺ and its metabolite levels in human blood in a dose-dependent manner, which directly supports anti-aging mechanisms. NMN also has good safety for long-term anti-aging use—no serious adverse reactions have been observed even at a single dose of up to 1250mg/day. In practical use, many users report feeling significantly more energetic and experiencing improved sleep quality after taking NMN, which are key indicators of enhanced cellular vitality related to anti-aging.
In contrast, there are relatively few clinical studies on direct NAD⁺ supplementation for anti-aging, and existing data show unsatisfactory results. Due to its extremely low absorption efficiency, even high-dose NAD⁺ intake rarely significantly increases intracellular NAD⁺ levels, making it unable to effectively activate anti-aging pathways. Additionally, the breakdown products of NAD⁺ may accumulate in the body, and long-term high-dose NAD⁺ intake may burden metabolic processes, posing higher safety risks for those seeking long-term anti-aging benefits.
After reviewing the above comparisons of NMN and NAD⁺ for anti-aging, the choice becomes clear. Here are specific recommendations based on your anti-aging needs and goals:
If your core need is to "efficiently supplement NAD⁺ and delay aging"—whether for daily anti-aging maintenance or to improve age-related issues like decreased energy and slowed metabolism that hinder your anti-aging goals—NMN is the better choice. This is especially true for the following groups seeking anti-aging benefits:
People over 30: After the age of 30, NAD⁺ levels in the body start to decline significantly, accelerating aging signs. Timely NMN supplementation helps maintain cellular vitality by boosting NAD⁺ levels and slow down the signs of aging;
People who stay up late or face high pressure: Long-term staying up late and overwork accelerate NAD⁺ consumption, which worsens aging signs, leading to low energy and weakened immunity. NMN supplementation can quickly increase NAD⁺ levels, relieve fatigue, and support anti-aging efforts;
People concerned about skin anti-aging: NAD⁺ promotes the metabolism and repair of skin cells, which is key for skin anti-aging. NMN supplementation helps improve age-related skin issues like skin sagging and dullness, making the skin look more vibrant and youthful;
Unless explicitly advised by a professional doctor for specific health conditions, ordinary people should avoid oral NAD⁺ supplements for anti-aging. On one hand, the NAD⁺ absorption efficiency is too low to achieve the expected anti-aging effect; on the other hand, long-term high-dose NAD⁺ intake may burden metabolism and pose potential safety risks. If you want to supplement NAD⁺-related active ingredients for anti-aging, opt for more absorbable alternatives like NMN or NR (nicotinamide riboside, another NAD⁺ precursor that supports anti-aging by boosting NAD⁺ levels).
Regardless of which NAD⁺ supplement you choose for anti-aging, you must follow the principle of "scientific supplementation" and avoid these common anti-aging misconceptions:
1.Higher NMN dosage is not better for anti-aging: The recommended daily dosage of NMN for anti-aging is generally 100-500mg, which should be adjusted based on age, weight, and health status. Excessive NMN intake may instead burden the body and undermine your anti-aging efforts;
2. Always choose regular NMN or NAD⁺ supplement products: With the booming anti-aging supplement market, product quality varies greatly. It’s recommended to choose NMN or NAD⁺ products with third-party testing certifications, transparent ingredients, and compliant production processes to ensure you’re getting effective, safe ingredients for your anti-aging goals;
3. Don’t rely solely on NMN or NAD⁺ supplements for anti-aging: Supplements only play an auxiliary role in anti-aging. Combining NMN supplementation with regular sleep, a balanced diet, and moderate exercise will yield better anti-aging results by maximizing NAD⁺’s effectiveness in your body;
In the end, the core difference between NMN and NAD⁺ for anti-aging lies in "whether they can efficiently reach cells and supplement active NAD⁺ to drive anti-aging effects". NAD⁺ itself is beneficial for anti-aging, but it cannot be directly absorbed and utilized by the human body—it can only serve as the ultimate target we want to supplement for anti-aging. As a direct precursor of NAD⁺, NMN can efficiently enter cells and be converted into NAD⁺, making it a more reliable and efficient choice for NAD⁺ supplementation and anti-aging currently.
The key to effective anti-aging is "science and precision". Choosing the right NAD⁺ supplement—NMN over direct NAD⁺ for most people—based on your own anti-aging needs allows these cutting-edge biotechnologies to truly benefit your health. We hope this breakdown of NMN vs NAD⁺ helps you clarify your thoughts, avoid anti-aging misconceptions, and find the anti-aging approach that suits you best.