In the field of anti-aging research, Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), a precursor of NAD⁺, is gaining significant attention from the scientific community. In September 2023, a national invention patent (Patent No.: 202311230678.4) on the application of NR in delaying aging was officially published. This patent, collaboratively completed by several domestic research institutions, systematically demonstrated the potential of NR in improving mitochondrial function and delaying cellular and tissue aging based on fundamental biology and various premature aging models. The research spans multiple dimensions, from the cellular level to the organ level, providing crucial technical support for the application of NR.

The patent research indicates that NR can improve mitochondrial status and enhance cell activity in various premature aging cell models. In the Cockayne Syndrome stem cell (CS hMSCs) model, NR significantly reduced the proportion of SA-β-gal positive cells, a typical marker of cellular aging. Additionally, in human arterial endothelial cells (hAECs), NR increased the cells’ self-renewal capacity. These data support the positive role of NR in maintaining cellular function and delaying aging, particularly in regulating energy metabolism and cell renewal, demonstrating stable effects.
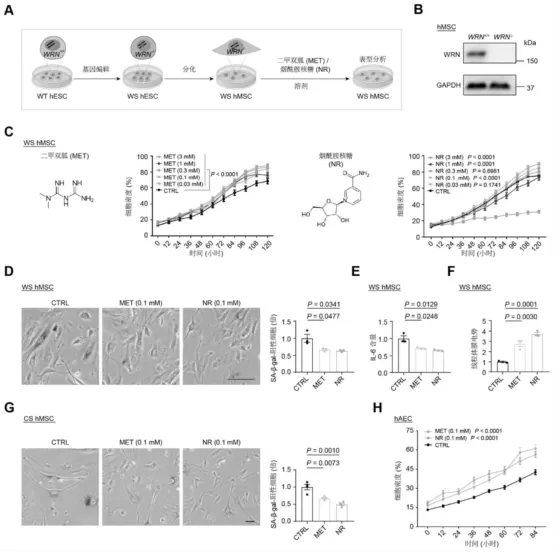
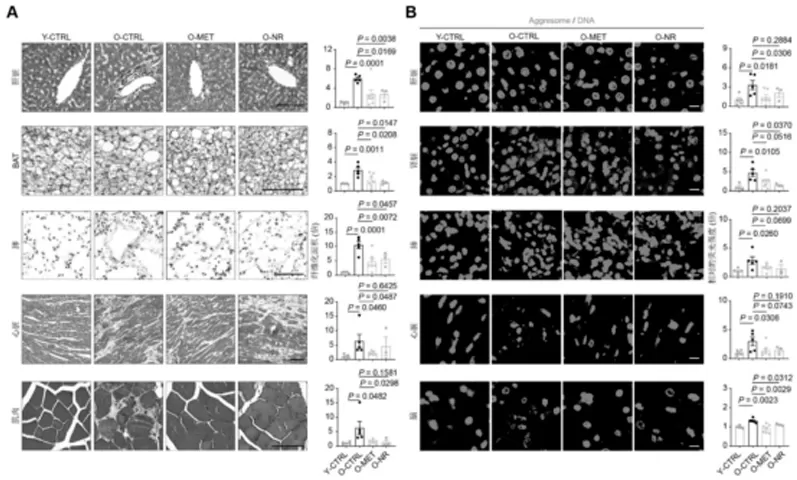
Beyond its cellular-level benefits, NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) demonstrates significant anti-aging capabilities across various organs and tissues. Long-term use of NR has been shown in animal models to slow the fibrosis process in multiple organs, including brown fat, heart, muscle, lungs, and liver. Additionally, the following effects have been observed: reduction in the aggregation of protein aggregates (aggresomes) in brain, heart, lung, liver, and kidney tissues; decrease in lipid droplet size in brown fat; reduction in glomerular and alveolar areas; decreased vascular wall thickness; reduced inflammatory cell infiltration in the liver; downregulation of inflammatory cytokine expression; and alleviation of chronic inflammation in multiple organs. These findings indicate that NR plays a role in various aging-related pathways and can, to some extent, delay degenerative changes in tissues and organs.
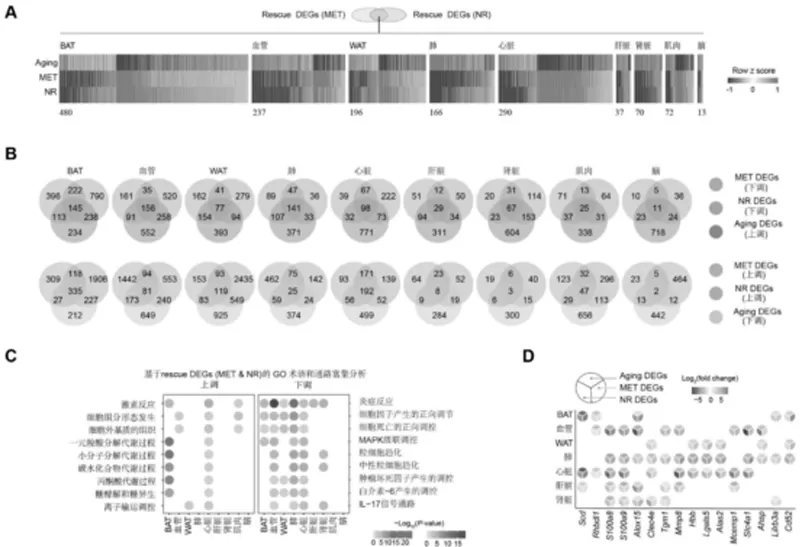
Bioinformatics analysis has further revealed the differential gene expression changes at the tissue level induced by NR. Data indicate that tissues such as white adipose tissue (WAT), blood vessels, and the heart are more responsive to NR treatment, with over 18% of aging-related genes being reversed under NR intervention. Notably, NR significantly downregulated various transcription factors related to inflammation and immune response (such as Cebpb, Rela, Stat2), thereby inhibiting chronic inflammatory responses at the gene regulation level. This regulatory mechanism not only enhances the stability of NR in aging intervention but also demonstrates its tissue-targeting characteristics as an intervention method.
Unlike some anti-aging compounds, long-term use of NR in animal models has not shown significant side effects. Studies indicate that NR’s tissue-targeting and regulatory mechanisms are relatively clear, with controllable risk of side effects, laying a solid foundation for its application in functional foods, nutritional supplements, and medical raw materials. Bontai Bioengineering (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd., as one of the early domestic companies to engage in NAD⁺ precursor materials, has accumulated extensive experience in the production and technical optimization of NR raw materials. Their nicotinamide riboside bulk raw material products feature high purity, low impurities, and customizable specifications, meeting a wide range of needs from dietary supplements to research purposes. With the gradual disclosure of more NR patent technologies and the technical improvements by upstream raw material companies in the industry chain, the technological maturity of NR is increasing, and its role in human health intervention is expected to become clearer and more defined.

As a key precursor in the NAD⁺ metabolic pathway, NR has transitioned from basic research to patent protection, demonstrating multidimensional anti-aging potential at both the tissue and gene levels. Driven by both scientific research and industry, its application in the field of healthy aging is gradually moving towards preclinical validation and actual product development. For individuals concerned with cellular health, tissue function, and chronic inflammation control, NR is expected to become a more standardized and scientifically-backed nutritional intervention option in the future.